In the first episode of this two-fer on the economics of conservation, we talk with Jeff Hadachek, Extension Specialist and Assistant Professor of Ag Economics at UW-Madison, to get the economist’s take on why economics is a useful tool when talking about conservation practices and adoption.
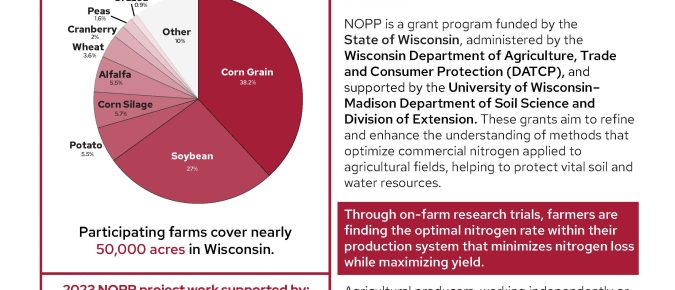
This report provides a glance at projects funded in the 2023 Nitrogen Optimization Pilot Program grant cycle and the people and farms behind them.
Dr. Mallika Nocco, UW-Madison Extension specialist in agrohydrology, and Landon Baumgartner, outreach specialist for the UW-Madison Extension Nutrient and Pest Management program for Southwest Wisconsin discuss the basics of buffer strips, their function, and how they could fit on your farm.
The July 24 Badger Crop Connect webinar featured Dr. Damon Smith, Extension field crops pathologist and Professor in the Department of Plant Pathology, University of Wisconsin–Madison. Damon gives an update on what diseases he’s seeing in Wisconsin farm fields in late July 2024. He mainly discusses white mold in soybean and tar spot in corn and management practices for each.
Harvesting small grains or processing crops in the summer months provides a great opportunity to plant a variety of cover crop species that can achieve several different benefits or goals such as soil erosion protection, nitrogen (N) supply to subsequent grain crops, and weed suppression.
Did you just harvest your wheat? Are you looking to maximize the benefits of manure applied to your wheat fields? What about capturing the additional growing degree days and planting a cover crop after your wheat is harvested? Check out our latest Bumper Crop video on essential tips for manure applications and cover crops after wheat harvest!
July is National Corn Month! Watch this new Bumper Crop video highlighting and appreciating one of America’s most versatile and essential crops and current research exploring the future of corn production.
Michael Geissinger and Chris Clark, outreach specialists for the UW-Madison Extension Nutrient & Pest Management Program, meet at the field to talk about micronutrient deficiencies including how to assess if your crops have micronutrient deficiencies and research on whether or not applying foliar micronutrient fertilizer in season can correct them.
The July 10 Badger Crop Connect webinar featured Jose Franco, a research agronomist with the U.S. Dairy Forage Research Center (USDA). Jose summarized current research efforts at the U.S. Dairy Forage Research Center on cover crops and continuous living cover. Ongoing research includes cover crop breeding efforts, work on alternatives to winter cereal rye following corn silage and some of the benefits of including flowering cover crops, and a whole systems approach to dairy forage systems evaluations.
The July 10 Badger Crop Connect webinar featured Dane Elmquist, a conservation cropping outreach specialist in the UW–Madison Division of Extension Agriculture Institute. Dane gave an overview of the Wisconsin Cover Crop Citizen Science network and highlighted project results. He also showcased the project’s interactive data dashboard and provided information on how to participate in the project for the 2024-2025 season.
From severe drought to flooded fields, Wisconsin’s forage producers are turning to forage species that can provide adaptability and flexibility in the midst of abnormal conditions. We jump in with Yoana Newman, UW-River Falls professor and Extension forage specialist, and Matt Oehmican, from Short Lane Ag Supply, to talk the details of warm season annual forages, from the decision-making process for growing these species to the unique technical agronomy management warm season annuals need to grow in Wisconsin.
The June 12 Badger Crop Connect webinar features Dr. Natasha Rayne, a new Extension faculty specialist in soil fertility. Dr. Rayne introduces us to her and her work and research in soil fertility.