Articles
▶ On-Farm Research 101: From hypothesis to harvest
Learn about the value of on-farm trials and discover practical approaches to implementing research projects tailored to your specific farming conditions.
Herbicide rotational restrictions, weed control, and cereal rye for forage
Cereal rye can be used as high-quality forage for livestock, but careful management of herbicide rotational intervals is essential to ensure legal and effective use.
Early season insect scouting in soybean
It’s almost time to scout for early season insect pests in corn and soybeans. These pests can impact soybean crops above and below ground.
Early season insect scouting in corn
It’s almost time to scout for early season insect pests in corn and soybeans. These pests can impact corn crops above and below ground.
How to lower phosphorus levels in Wisconsin crop fields
High soil test phosphorus is a challenging issue that requires a combination of strategies for long-term nutrient management. Start here to understand all the tools you have in your phosphorus management toolbox.
Evaluating alfalfa stands for profit in spring 2025
Alfalfa stand quality can (and should!) be evaluated in both spring and fall. Fall evaluations have the advantage of giving us more time to make management decisions for the following growing season, such as fertilizer application, spring herbicide strategies, and crop sequencing. Learn what to look for in this article.
Field Notes Episode 25: Good Bugs and Planting Naked Seed
Treated seed is the default for planted soybean (60-80%) and especially corn (close to 100%) acres across the US. While there are certainly advantages to some seed treatments, especially fungicidal treatments for early planted soybeans, others like insecticidal seed treatments can have a negative effect on the beneficial insects–aka good bugs–that prey on major pests in agricultural fields. Some farmers in a bid to save some money and help out the beneficials have gone back to planting naked seed.
Research Brief: Interseeding legumes into grass pastures
While legume longevity can be improved through grazing and fertility management, it is a common practice to reseed legumes every few years. This is often achieved by interseeding into established pastures by no-till drilling or frost-seeding. Each method has unique benefits and drawbacks.
Creating New Opportunities for Wisconsin Farmers Through the UW Emerging Crops Team and WI Emerging Crops Coalition
This Strategic Plan outlines key development priorities to advance each crop based on extensive input and analysis from early-adopter growers and stakeholders working to develop the crop.
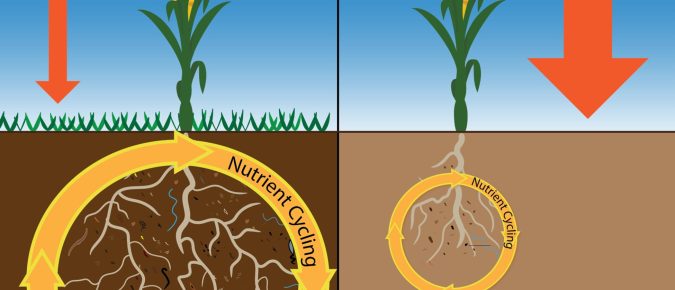
Soil Health in Wisconsin: Characteristics of Healthy Soil
This article highlights the characteristics of healthy soil and describes how these characteristics, and soil health generally, can contribute to sustainable crop production and indirectly impact society beyond the farm field.